Gum diseases are a common oral health problem that affect millions of people worldwide. They are caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria in the mouth, which can lead to inflammation and infection of the gums. Two of the most common types of gum diseases are gingivitis and periodontitis, which can have serious consequences if left untreated. While gum diseases are often associated with poor oral hygiene, they can also be caused by a variety of other factors, such as genetics, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. In this Overview of Gum Diseases article, we will provide an overview of gum diseases, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. We will also discuss the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene and lifestyle habits to prevent the development of gum diseases. By understanding the basics of gum diseases, you can take steps to protect your oral health and overall well-being.

An Overview Of Gum Disease
The etiology of gum diseases, including gingivitis and periodontitis, is multifactorial and involves various risk factors such as bacterial plaque, host response, and environmental factors. Bacterial plaque is a biofilm that forms on the teeth and gums and contains bacteria that can cause inflammation and damage to the gums. Host response refers to the body’s immune response to the presence of bacterial plaque, which can vary between individuals and affect the severity of gum disease. Environmental factors, such as smoking, poor nutrition, and stress, can also contribute to the development and progression of gum disease.
It is important to note that the presence of bacterial plaque is a necessary, but not sufficient, condition for the development of gum disease. Other factors, such as genetic predisposition and systemic diseases, can also play a role in the onset and severity of gum disease. Understanding the complex etiology of gum disease is crucial in developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. In the following section, we will explore the symptoms of gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease.
The Symptoms of Gingivitis
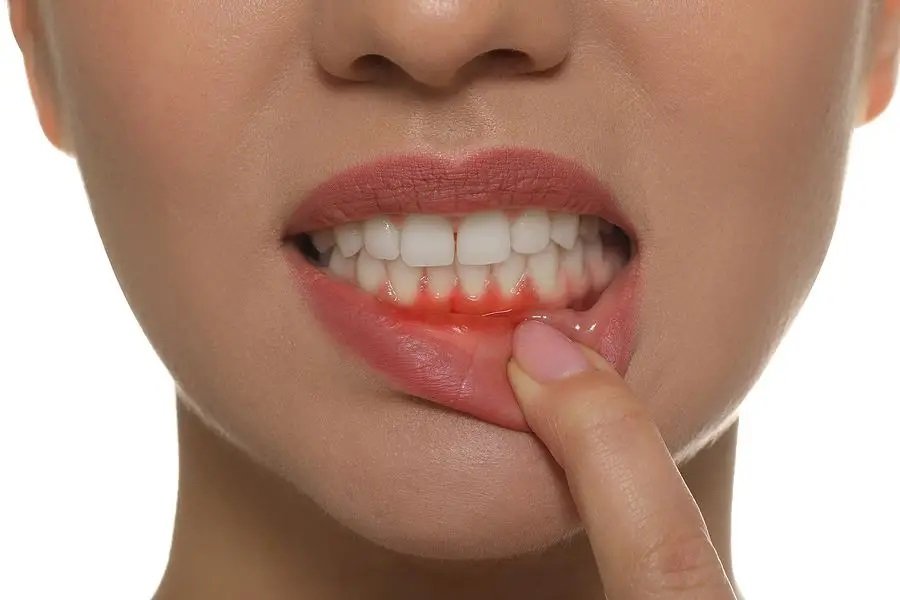
One of the most common signs of early-stage gum disease is the presence of red, swollen, and tender gums. As the disease progresses, the gums may become more sensitive and bleed easily during brushing or flossing. Other symptoms of gingivitis include bad breath, receding gums, and the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums.
It is important to note that not all cases of gingivitis show visible symptoms, which is why regular dental checkups are crucial. In the next section, we will discuss how to diagnose gum diseases and the importance of seeking early treatment.
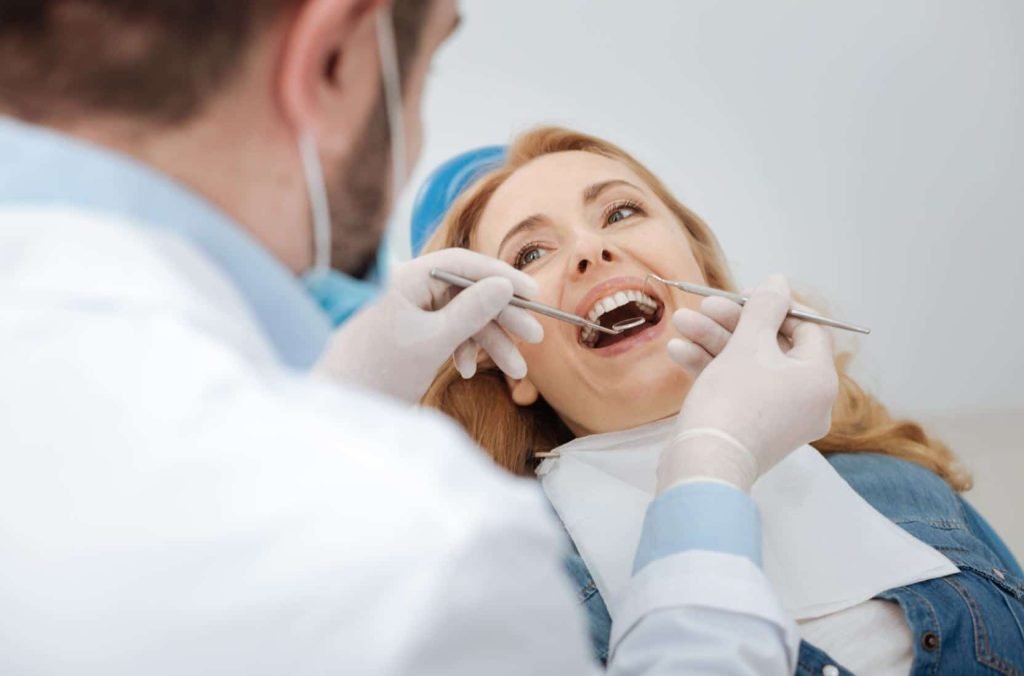
How to Diagnose Gum Diseases
Diagnosing gum diseases requires a thorough examination of the teeth, gums, and surrounding tissues, as well as taking into account a patient’s medical history and risk factors. The first step in diagnosing gum disease is a visual examination of the gums, looking for signs of inflammation, bleeding, or recession. The dentist or periodontist may also use a probe to measure the depth of the pockets between the teeth and gums, which can indicate the extent of gum disease. X-rays may also be taken to check for bone loss, which can occur in more advanced cases of periodontitis.
In addition to these methods, the dentist or periodontist may also ask about the patient’s medical history and lifestyle factors that can increase their risk for gum disease, such as smoking, diabetes, or a family history of the condition. By taking into account all of these factors, a proper diagnosis can be made and a treatment plan can be developed to address the specific needs of the patient. The consequences of untreated gum diseases can be severe, leading to tooth loss, chronic infections, and other health complications, which we will discuss in the subsequent section.
The Consequences of Untreated Gum Diseases
Untreated gum diseases can result in serious consequences that extend beyond the oral cavity. When left untreated, gingivitis can progress into periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that affects the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums, bone, and ligaments. Periodontitis can cause tooth loss and bone destruction, leading to a decrease in jawbone density and a change in facial structure. Moreover, research has shown that periodontitis can increase the risk of developing systemic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
The consequences of untreated gum diseases are not limited to physical health but can also affect one’s self-esteem and mental health. Chronic bad breath, bleeding gums, and missing teeth can cause embarrassment and affect one’s ability to socialize and communicate effectively. Additionally, the pain and discomfort associated with gum diseases can cause anxiety and depression, leading to a decrease in the quality of life. Therefore, it is crucial to seek treatment for gum diseases promptly. In the subsequent section, we will discuss the connection between gum diseases and other health problems.

The Connection Between Gum Diseases and Other Health Problems
The correlation between poor oral health and systemic diseases has been a subject of interest in recent research. Studies have shown that gum diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, may increase the risk of developing other health problems. These health problems include heart disease, stroke, diabetes, respiratory diseases, and even certain types of cancers.
The exact mechanism behind the link between gum diseases and these health problems is still not fully understood. However, it is believed that the bacteria that cause gum diseases can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, causing inflammation and damage. This can then lead to the development of other health problems. Therefore, it is important to not only treat gum diseases for the health of your mouth, but also for the overall health of your body.
As we understand the potential risks associated with untreated gum diseases, it is important to learn about the different ways to treat them. In the subsequent section, we will explore some of the effective at-home remedies for treating gingivitis.
Treating Gingivitis: At-Home Remedies
Research suggests that there is a link between gum diseases and other health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory issues. Therefore, taking care of our oral health is important not only for our dental hygiene but also for our overall health and well-being. In this section, we will focus on treating gingivitis, a common gum disease that affects many individuals.
Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums caused by bacteria that accumulate in the plaque that forms on teeth. Common symptoms include redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. Fortunately, gingivitis can be treated at home through various remedies. Maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly is key. Additionally, using an antiseptic mouthwash and avoiding tobacco products can also help alleviate symptoms. These at-home remedies can improve the health of one’s gums and prevent the progression of gingivitis.
As important as at-home remedies are, it is essential to recognize that professional treatment options are available for those with gum diseases. In the next section, we will explore the different types of professional treatment options for individuals with gingivitis and periodontitis.

Professional Treatment Options for Gum Diseases
Professional treatment options for gum diseases include various methods that can be effective in improving the health of one’s gums and preventing further progression of the disease. One of the most common professional treatments for gum diseases is scaling and root planing. This procedure involves removing the plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and the root surfaces, which helps reduce the inflammation of the gums. The dentist or periodontist may use local anesthesia to numb the gums during the procedure. The patient may also receive antibiotics to control the infection and reduce the risk of further damage to the gums and teeth.
Another professional treatment option for gum diseases is periodontal surgery. This procedure is usually recommended for patients with advanced stages of periodontitis, where the gum tissues and bone have been severely damaged. The surgery involves removing the infected gum tissues and bone, and then grafting new tissues and bone onto the affected areas. This helps restore the structure and function of the gums and teeth. However, periodontal surgery is a more invasive procedure and requires a longer recovery period than scaling and root planing. To prevent gum diseases, it is important to practice good oral hygiene habits and visit the dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings.
Preventing Gum Diseases: Best Practices for Oral Hygiene
Maintaining consistent oral hygiene practices can significantly reduce the risk of developing and worsening gum conditions. Brushing teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash can help remove plaque and food particles that can lead to gum disease. It is also important to replace toothbrushes every three to four months and avoid using tobacco products, which can increase the risk of gum disease.
In addition to regular oral hygiene practices, scheduling regular dental check-ups can help detect and prevent gum disease. Dentists can perform professional cleanings, monitor changes in gum health, and provide personalized recommendations for maintaining oral health. By prioritizing oral hygiene and seeking professional dental care, individuals can reduce their risk of developing gum disease and maintain a healthy smile for years to come. This sets the foundation for the subsequent section about ‘diet and lifestyle tips for preventing gum diseases,’ which can further enhance oral health.

Diet and Lifestyle Tips for Preventing Gum Diseases
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices is undoubtedly the most effective way to prevent gum diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis. However, there are other lifestyle factors that can contribute to the development of gum diseases, including diet and lifestyle choices.
A healthy diet that is low in sugar and high in nutrients can help to prevent gum disease. Foods that are high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and leafy greens, can strengthen the gums and prevent them from becoming inflamed. Additionally, drinking plenty of water can help to flush out harmful bacteria from the mouth and prevent plaque buildup. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also help to prevent gum disease, as these habits can weaken the immune system and make it more difficult for the body to fight off infections. By making positive choices in regards to diet and lifestyle, individuals can greatly reduce their risk of developing gum disease.
As with any health condition, early detection and treatment is key to preventing further damage. In the next section, we will discuss when it is essential to seek dental treatment for gum disease.
When to See a Dentist for Gum Disease Treatment
Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial in managing the progression of gum disease, ensuring optimal oral health. If you notice any changes in your gum health, it is important to schedule an appointment with your dentist immediately. Some of the signs of gum disease include bleeding gums, swollen or red gums, bad breath, loose teeth, and receding gums. The earlier you seek treatment, the better your chances are of reversing the damage and preventing further complications.
Your dentist will assess the severity of your gum disease and recommend the appropriate treatment plan. This may include scaling and root planing, antibiotic therapy, or surgical intervention. In addition to professional treatment, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene habits and follow a healthy diet and lifestyle to prevent the recurrence of gum disease. By taking proactive steps to manage your gum health, you can enjoy a healthy, beautiful smile for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can gum diseases be inherited genetically?
Research suggests that genetics may play a role in the development of gum disease, but it is not the sole factor. Environmental and lifestyle factors also contribute. Regular dental care and healthy habits can help prevent or manage gum disease regardless of genetic predisposition.
What is the role of stress in causing gum diseases?
Stress can contribute to gum disease by suppressing the immune system and increasing inflammation. However, the relationship between stress and gum disease is complex and further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms involved.
Is there a correlation between gum diseases and smoking?
Research has shown a clear correlation between smoking and gum diseases. Smokers have a higher risk of developing gingivitis and periodontitis, and the severity of these conditions is directly related to the frequency and duration of smoking. Quitting smoking can improve oral health.
Are there any natural remedies for treating gum diseases?
Several natural remedies have been suggested for treating gum diseases, including oil pulling, herbal mouth rinses, and saltwater gargles. However, more research is needed to determine their effectiveness, and they should not replace professional dental care.
Can certain medications increase the risk of developing gum diseases?
Certain medications such as anticonvulsants, immunosuppressants, and oral contraceptives have been linked to an increased risk of developing gum diseases. It is important to inform your dentist of any medications you are taking to ensure proper oral care.
Read more content about:
https://www.nutrition.gov/topics/basic-nutrition/healthy-eating
Final Verdict
In conclusion, overview of gum disease is a common oral health issue that affects many people. It is caused by the buildup of plaque and can lead to serious consequences if left untreated. Symptoms of gum disease include bleeding gums, bad breath, and gum recession. Diagnosis is typically done through a physical exam and x-rays. Professional treatment options include deep cleaning, medication, and surgery, while preventing gum disease involves maintaining good oral hygiene and adopting a healthy lifestyle.
It is important to understand the connection between gum disease and other health problems, such as heart disease and diabetes, as this can have significant implications for overall health. Therefore, it is crucial to seek professional treatment at the first sign of gum disease and to maintain good oral hygiene practices to prevent its onset. By taking proactive measures, individuals can improve their oral health and reduce the risk of developing gum disease and other health issues.


