Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common dental problem that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a bacterial infection that affects the tissues that surround and support the teeth, causing inflammation, bleeding, and eventually tooth loss if left untreated. Let’s explore in detail Importance of Early Detection and Treatment Of Gum Disease. The prevalence of gum disease is increasing and is a significant public health concern globally.
Early detection and treatment of gum disease are crucial to prevent its progression and minimize its impact on oral and overall health. The consequences of untreated gum disease can be severe, leading to tooth loss, bone damage, and various systemic diseases. Therefore, it is essential to understand the causes, risk factors, signs, and symptoms of gum disease to ensure timely intervention and appropriate treatment. In this article, we will discuss the importance of early detection and treatment of gum disease and the measures that can be taken to prevent its occurrence and progression.
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the tissues supporting the teeth, such as the gums, ligaments, and bone. It is caused by the accumulation of bacterial biofilm on the tooth surface, which triggers an immune response that results in the destruction of the supporting tissues and bone over time. Gum disease can range from mild gingivitis, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums, to severe periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss.

The development of gum disease is influenced by several factors, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, genetic predisposition, systemic diseases, hormonal changes, and certain medications. It is important to understand the causes and risk factors of gum disease to prevent its onset and progression. By taking preventive measures and seeking early treatment, individuals can maintain good oral health and prevent the complications associated with gum disease.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors have been identified that increase the likelihood of developing gum disease, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, and certain medical conditions. Poor oral hygiene is the most common cause of gum disease. When teeth are not properly brushed and flossed, a sticky film of bacteria called plaque builds up on the teeth. If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into a substance called tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. Tartar buildup can cause inflammation and irritation of the gums, leading to gum disease.
Smoking is another major risk factor for gum disease. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the gums and reduce blood flow to the gums, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, can also increase the risk of gum disease. People with diabetes are more susceptible to infections, including gum infections, and have a harder time fighting off infections once they occur. These risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing gum disease, making early detection and treatment even more important.
As gum disease progresses, it can become more difficult to treat and can lead to serious complications. The next section will discuss the stages of gum disease and the potential consequences of leaving it untreated.
Stages of Gum Disease
One of the key factors in understanding the progression of periodontal infection is identifying the stages of gum disease. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a chronic bacterial infection that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It is a progressive condition that starts with mild inflammation of the gums and can eventually lead to the destruction of the bone that supports the teeth.
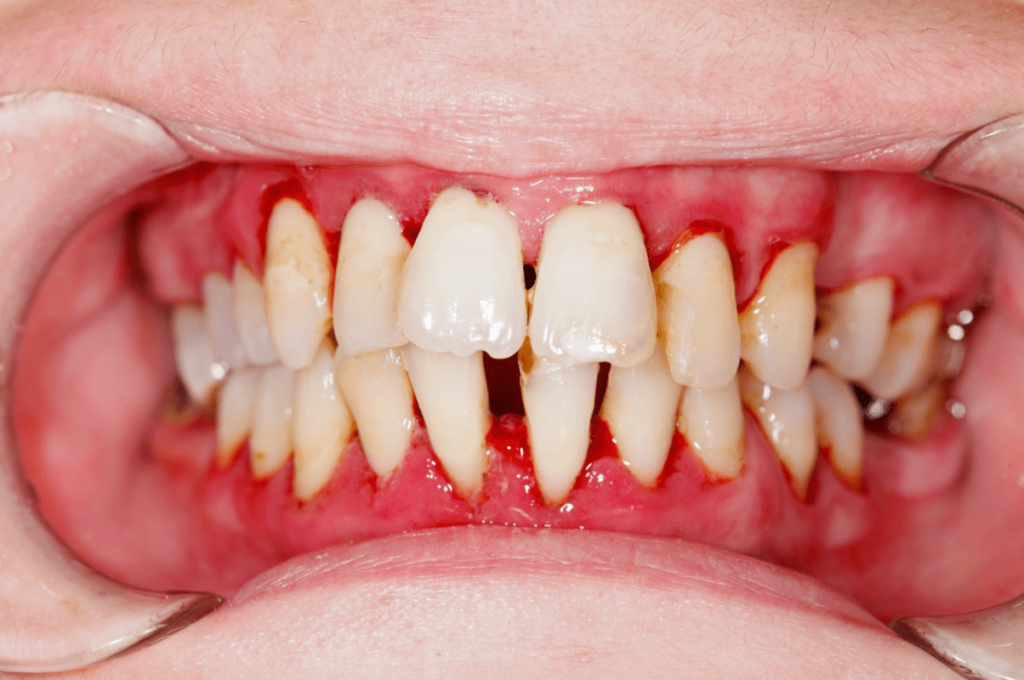
The stages of gum disease are classified as gingivitis, periodontitis, and advanced periodontitis. Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease and is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, where the bacteria and plaque buildup start to affect the bone and connective tissue that hold the teeth in place. Advanced periodontitis is the final stage of gum disease and is characterized by severe bone loss and tooth mobility. Identifying the stages of gum disease is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan to prevent further damage to the teeth and gums. In the subsequent section, we will discuss the signs and symptoms of gum disease in more detail.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
Identifying the presence of periodontal infection can be done by observing specific clinical signs and symptoms in the oral cavity. These can include red, swollen, or tender gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing, receding gums, loose teeth, persistent bad breath, and changes in the way teeth fit together when biting. It is important to note that gum disease can develop without any obvious signs or symptoms, which is why regular dental check-ups and cleanings are crucial for early detection and treatment.
If left untreated, gum disease can lead to serious complications such as tooth loss and bone damage. In addition, research has shown that gum disease may be linked to other health issues such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Therefore, it is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms of gum disease and seek prompt treatment to prevent further damage to oral and overall health.
Effects of Untreated Gum Disease
Untreated periodontal infection may result in severe dental and systemic complications, including bone loss, tooth decay, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. When gum disease is left untreated, it can lead to the destruction of teeth and gums, causing the teeth to loosen and fall out. The bacteria that cause gum disease can also spread to other parts of the body, causing inflammation and damage to organs such as the heart and kidneys.

In addition, untreated gum disease can lead to the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums, creating a space for bacteria to thrive. This can cause the gums to recede, exposing the roots of the teeth and making them more vulnerable to decay. Ultimately, the effects of untreated gum disease can be devastating, leading to a host of serious health problems. It is therefore crucial to detect and treat gum disease early on to prevent these complications from occurring.
Moving on to the next section about the diagnosis of gum disease, it is important to understand the various methods used by dental professionals to detect the disease.
Diagnosis of Gum Disease
Various techniques are employed by dental professionals to diagnose periodontal infection, including clinical examination, radiographic imaging, and measurement of periodontal pocket depths. During a clinical examination, a dentist or periodontist will inspect the gums and teeth for signs of swelling, inflammation, and bleeding. They will also evaluate the patient’s medical history, as certain conditions such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders can increase the risk of gum disease.
Radiographic imaging, such as X-rays, can help to identify bone loss and other underlying issues that may be contributing to gum disease. Additionally, measuring the depth of periodontal pockets can provide insight into the severity of the infection. These pockets are areas between the teeth and gums where bacteria can accumulate and cause damage. By measuring the depth of these pockets, dental professionals can determine the extent of the infection and create a treatment plan tailored to the patient’s needs. With an accurate diagnosis, patients can receive timely treatment to prevent further damage and improve their overall oral health.
Moving forward, effective treatment options for gum disease include both non-surgical and surgical interventions.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Effective management of periodontal infection involves a range of non-surgical and surgical interventions. Non-surgical treatment options include scaling and root planing, which involves the removal of plaque and calculus from the teeth and roots. This procedure is usually done under local anesthesia and may require multiple visits to complete. Another non-surgical option is the use of antibiotics, either as a pill or as a topical application. Antibiotics are used to control the bacterial infection and reduce inflammation. Surgical treatment options include flap surgery, which involves lifting the gum tissue to remove tartar and bacteria from the teeth and roots. In more advanced cases, bone and tissue grafts may be necessary to regenerate lost bone and tissue.

It is important to note that treatment alone is not enough to manage periodontal disease. Long-term maintenance, including regular dental visits, good oral hygiene habits, and healthy lifestyle choices, is necessary to prevent the disease from returning. In the next section, we will discuss the importance of prevention in maintaining good oral health.
Prevention of Gum Disease
Preventive measures, such as maintaining good oral hygiene habits and visiting the dentist regularly, play a crucial role in reducing the risk of developing periodontal disease. Brushing and flossing regularly removes plaque, the main cause of gum disease. It is recommended to brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss at least once a day. Additionally, using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce the bacteria that cause plaque and gum disease.
However, good oral hygiene habits alone may not be enough to prevent gum disease. Regular dental checkups are also important in preventing and detecting gum disease at an early stage. A dentist can identify and treat gum disease before it becomes more severe and causes irreversible damage to the teeth and gums. Therefore, it is recommended to visit the dentist at least twice a year for a regular dental checkup. In the subsequent section, we will discuss the importance of regular dental checkups and how they can help in early detection and treatment of gum disease.
Importance of Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups are crucial for maintaining optimal oral health and preventing the progression of dental issues. These checkups allow dentists to identify any potential problems early on, before they become more serious and difficult to treat. During a routine dental checkup, a dentist will thoroughly examine your teeth, gums, and mouth, looking for any signs of decay, gum disease, or other issues. They may also take x-rays to get a better look at what’s going on beneath the surface.
In addition to catching potential problems early, regular dental checkups also allow dentists to provide preventative care. This can include cleanings, fluoride treatments, and other measures to help keep your teeth and gums healthy. By staying on top of your dental health with regular checkups, you can lower your risk of developing serious oral health issues down the line. This sets the stage for maintaining good oral health overall and preventing the onset of gum disease.
Maintaining Good Oral Health
Regular dental checkups are essential for maintaining good oral health. During these checkups, dentists can identify any potential issues and provide appropriate treatment before they become more severe. However, maintaining good oral health goes beyond just scheduling regular dental appointments. It also involves taking care of your teeth and gums on a daily basis.
Good oral hygiene practices include brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen breath. Eating a balanced diet and limiting sugary and acidic foods can also help prevent tooth decay and gum disease. By taking good care of your teeth and gums, you can reduce your risk of developing gum disease and other oral health problems. This is especially important given the significant impact that gum disease can have on your overall health. In the next section, we will explore the importance of early detection and treatment of gum disease and why it is crucial to take action as soon as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can gum disease lead to other health issues besides oral health problems?
Research suggests a link between gum disease and systemic health issues such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. Early detection and treatment of gum disease may reduce the risk of developing these health issues.
What are the different types of treatment options available for gum disease?
Treatment options for gum disease include nonsurgical methods such as scaling and root planing, and surgical methods like gum grafts and flap surgery. Treatment depends on the severity of the disease and individual needs.
Is it possible to reverse the effects of gum disease with proper treatment and care?
Research suggests that with proper treatment and care, it is possible to reverse the effects of gum disease. However, the success of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and the patient’s commitment to maintaining good oral hygiene practices.
How often should I schedule dental checkups to prevent or detect gum disease?
Regular dental checkups should be scheduled every six months to prevent or detect gum disease. This is crucial as early intervention can prevent irreversible damage and tooth loss. It is recommended that individuals with a higher risk profile visit more frequently.
Can genetics play a role in the development of gum disease?
Yes, genetics can play a role in the development of gum disease. Studies suggest that certain genes can increase susceptibility to periodontitis. However, good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups can help prevent and manage the disease.
Find more info about:
https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/health-disease/cardiovascular-disease
Resolution
In resolution, importance of early detection and treatment of gum disease is crucial in maintaining good oral health. The causes and risk factors of gum disease should be well understood in order to prevent its occurrence. Regular dental checkups and practicing good oral hygiene are effective ways of preventing gum disease. In the event that gum disease does occur, prompt treatment is necessary to prevent further complications such as tooth loss, infections, and even systemic health problems.
It is important for individuals to prioritize their oral health and seek professional dental care as needed. With early detection and treatment, the negative effects of gum disease can be avoided, and individuals can maintain healthy teeth and gums for years to come. Overall, the importance of early detection and treatment of gum disease cannot be overstated, and should be a priority for all individuals seeking to maintain good oral health.

