Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by bacteria that build up on the teeth and gums, leading to inflammation and infection. If left untreated, gum disease can cause serious damage to the teeth and gums, eventually leading to tooth loss. Understanding the Signs and Symptoms of gum disease is essential for maintaining good oral health and preventing serious complications. Despite its prevalence, many people are unaware of the signs and symptoms of gum disease. This signs and symptoms of gum disease article aims to provide a brief overview of gum disease, including its early and advanced stages, common symptoms, risk factors, and prevention and treatment options. By understanding the signs and symptoms of gum disease, readers can take proactive steps to protect their oral health and prevent serious complications down the line.

Understanding Gum Disease: A Brief Overview
A comprehensive understanding of gum disease can be obtained through an overview of its signs and symptoms. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and underlying bone that hold teeth in place. It is caused by bacterial infection that leads to inflammation and damage to the gums.
The early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis. It is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums, and it can be reversed with proper oral hygiene. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which is a more severe form of gum disease. Understanding the signs and symptoms of gum disease is essential for early detection and prompt treatment.

Gingivitis: The Early Stage of Gum Disease
The early stage of periodontal disease, known as gingivitis, is characterized by inflammation and bleeding of the gums due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. This condition is caused by poor oral hygiene practices, which lead to the formation of plaque and tartar. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that accumulates on teeth, and if left untreated, it can harden into tartar. The bacteria in plaque and tartar can cause an infection that leads to inflammation of the gums, which is the hallmark of gingivitis. Click here to read more about gum disease
Early detection and treatment of gingivitis are crucial to prevent the progression of the disease to more severe forms of periodontal disease. Symptoms of gingivitis can range from mild to severe and may include red, swollen, and bleeding gums, bad breath, and a bad taste in the mouth. In the next section, we will explore the signs and symptoms of gingivitis in more detail.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
Detecting early stages of periodontal disease can be challenging, but understanding the various indications of gingivitis is crucial to maintaining good oral health. The early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis, which is characterized by swollen, red, and bleeding gums. Gingivitis is caused by the accumulation of plaque and bacteria on the teeth, which irritates the gums and causes inflammation. In some cases, gingivitis may not cause any discomfort, making it easy to overlook. However, the symptoms of gingivitis should not be ignored, as they can lead to more serious oral health problems if left untreated.
Some of the symptoms of gingivitis include bleeding gums when brushing or flossing, bad breath, receding gums, and tender or swollen gums. It is important to note that these symptoms may not always be present, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings can help detect and treat gingivitis early, before it progresses into more advanced stages of gum disease. If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to periodontitis, which is a more serious form of gum disease characterized by bone loss and tooth loss. To prevent periodontitis, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene habits and seek professional dental care when necessary.
As gingivitis progresses into periodontitis, the symptoms become more severe and may include pus between the teeth and gums, loose teeth, and changes in bite alignment. It is important to seek professional treatment as soon as possible if you are experiencing any of these symptoms. In the next section, we will discuss periodontitis in more detail and how it differs from gingivitis.

Periodontitis: Advanced Gum Disease
Periodontitis is an advanced stage of periodontal disease that is characterized by the breakdown of the tissues that support the teeth. When gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress into periodontitis. The bacterial infection starts to spread deeper into the gums, causing them to pull away from the teeth. This creates small pockets that trap more bacteria, which can result in further damage to the gums and bone that supports the teeth.
As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen and the bone and gum tissue continue to recede. The teeth may become loose and even fall out in severe cases. Periodontitis is a serious condition that requires immediate attention from a dental professional. Without proper treatment, it can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. In the next section, we will discuss the symptoms of periodontitis in detail.
Signs and Symptoms of Periodontitis
One indicator of advanced periodontal disease is the loss of attachment between the gums and teeth. This occurs when the bacteria in plaque and tartar build up on the teeth and gums, causing inflammation and damaging the tissue that connects the teeth to the gums. As a result, the gums begin to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets that become infected and can lead to bone loss. Other symptoms of periodontitis include bleeding gums, bad breath, loose teeth, and changes in the bite.
Periodontitis can cause significant damage to the teeth and gums if left untreated. In addition to tooth loss and gum recession, it has also been linked to a variety of other health issues, including heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. It is important to seek treatment for gum disease as soon as possible to prevent further damage and improve overall health. In the next section, we will discuss the connection between gum disease and your overall health.
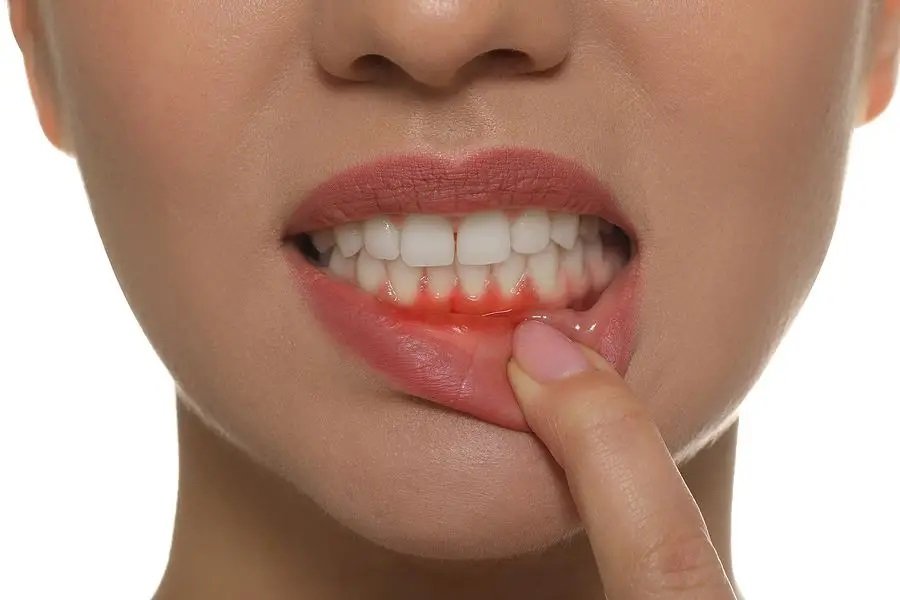
Gum Disease and Your Overall Health
The relationship between periodontal health and systemic health has been a topic of interest in the medical and dental fields for many years. Research has shown that there is a potential link between gum disease and other health conditions such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and respiratory diseases. The exact nature of this relationship is still being studied, but some theories suggest that the inflammation caused by gum disease may contribute to these other health problems.
It is important to note that the link between gum disease and systemic health is not yet fully understood, and more research is needed to establish causality. However, it is clear that maintaining good oral hygiene and treating gum disease promptly can have a positive impact on overall health. In the next section, we will discuss some of the risk factors for gum disease and how they can be managed.
Risk Factors for Gum Disease
Several factors have been identified that increase the risk of developing periodontal disease. The most common risk factor is poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque to form on the teeth and gum line. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that can cause inflammation of the gums, leading to gingivitis and periodontitis if left untreated. Other factors that increase the risk of developing gum disease include smoking, genetics, hormonal changes in women, certain medications, and health conditions such as diabetes and HIV.
It is important to identify these risk factors and take steps to mitigate them in order to prevent the development of gum disease. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings, proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing, and a healthy diet that is low in sugar and high in nutrients can all help reduce the risk of gum disease. In the next section, we will discuss the prevention and treatment options available for those who have already developed gum disease.
Prevention and Treatment of Gum Disease
Implementing proper oral hygiene practices and seeking professional dental care are effective measures in preventing and treating periodontal conditions, promoting healthy gums and teeth. Brushing teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste helps eliminate plaque and bacteria buildup that cause gum inflammation and bleeding. Flossing at least once a day removes food particles and plaque between teeth and along the gum line that a toothbrush cannot reach. Using an antiseptic mouthwash can also reduce bacteria and freshen breath. Additionally, proper nutrition and avoiding smoking can also contribute to gum health.

When gum disease is already present, professional dental care is necessary to treat it. A dentist or periodontist can perform a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing, which involves removing tartar and bacteria from below the gum line and smoothing out rough spots on tooth roots to help prevent future buildup. In more severe cases, surgery may be needed to repair damage and restore gum health. Early detection and treatment of gum disease is crucial in preventing irreversible damage and tooth loss. Therefore, regular dental check-ups are essential in maintaining optimal oral health.
Importance of Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are a vital aspect of maintaining optimal oral health and preventing irreversible damage to teeth and gums. Although individuals may practice regular oral hygiene routines at home, professional dental cleanings and examinations are necessary to detect and address any potential issues before they become more severe. During a dental check-up, the dentist or dental hygienist will thoroughly clean and remove any plaque or tartar buildup that cannot be removed through regular brushing and flossing. They will also examine the teeth and gums for any signs of gum disease, tooth decay, or other dental issues.
In addition to cleaning and examining the teeth and gums, regular dental check-ups also serve as a preventative measure against more serious health issues. Research has shown a link between gum disease and other health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. By maintaining regular dental check-ups, individuals can catch any potential dental issues before they become more severe and possibly impact overall health. Taking action to prevent gum disease and maintaining regular dental check-ups can lead to a healthier and happier life.
Final Thoughts: Taking Action Against Gum Disease
Regular dental check-ups are essential in preventing and detecting gum disease. However, it is not always possible to avoid gum disease, and it is important to know the signs and symptoms to take action promptly. Gum disease is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss and even affect overall health, so it is important to be aware of the warning signs.
Some of the common signs of gum disease include redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums, bad breath, receding gums, and loose teeth. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to see a dentist as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment of gum disease can help prevent further damage to the gums and teeth. In addition to regular dental check-ups, maintaining good oral hygiene practices such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash can help prevent gum disease. Taking action against gum disease can help protect your dental and overall health, so don’t ignore the warning signs and seek professional help if needed.

Frequently Asked Questions
How does gum disease affect overall health?
Gum disease can lead to systemic health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. The inflammation caused by gum disease can increase inflammation in the body, leading to these conditions. Proper oral hygiene can help prevent gum disease and improve overall health.
Can gum disease be cured completely?
Gum disease can be treated, but there is no guarantee of a complete cure. It is a chronic condition that requires ongoing care to manage symptoms and prevent further damage. Regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene habits are essential.
Can gum disease cause tooth loss?
Untreated gum disease can indeed lead to tooth loss. As the disease progresses, it can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets where bacteria can accumulate and damage the supporting structures of the teeth.
Is gum disease hereditary?
Research shows that genetics can play a role in gum disease, with certain genes increasing susceptibility. However, lifestyle factors such as smoking and poor oral hygiene are still the primary causes. Proper dental care can help prevent and manage gum disease.
Can certain medications increase the risk of gum disease?
Certain medications, such as anticonvulsants, immunosuppressants, and calcium channel blockers, have been linked to an increased risk of gum disease. It is important for individuals taking these medications to maintain good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups.
Click here to read more info:
https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/oral-hygiene
https://www.hacc.edu/ProgramsandCourses/Dental-Hygienist.cfm
Closing Thoughts
Gum disease is a common oral health problem that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a preventable condition, and early detection and treatment can help prevent its progression. Understanding the signs and symptoms of gum disease is crucial in identifying and addressing the problem promptly. Gingivitis and periodontitis are the two stages of gum disease, and they manifest differently. Gingivitis is characterized by swollen and bleeding gums, while periodontitis involves bone loss and tooth mobility.
Prevention and treatment of gum disease involve adopting good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, and seeking professional dental care. Dental check-ups provide an opportunity to detect and address gum disease early. In conclusion, gum disease can have severe consequences if left untreated, including tooth loss and other health complications. Therefore, it is essential to take preventive measures and seek professional dental care promptly to maintain healthy gums and teeth.


